Fortinet Data Breach: A Wake-Up Call
Fortinet, a leading global cyber security firm, confirmed a data breach involving unauthorised access to a third-party cloud-based shared file drive, affecting less than 0.3% of its customers. The attacker, using the name "Fortibitch," claimed to have stolen 440 GB of sensitive data, which they later shared online. Fortinet quickly responded by terminating unauthorised access, launching an internal investigation, and engaging law enforcement and cyber security agencies. No evidence of customer targeting, or malicious activity has been found, and Fortinet’s operations remain unaffected.
The company launched an internal investigation to assess the extent of the data breach and determine how the attacker gained access to its systems. They promptly terminated the unauthorised access route used by the intruder and reported the incident to law enforcement agencies and cyber security response teams for further assistance.


Broader trends in cyber attacks, including ransomware and supply chain breaches, signal the increasing threat facing all industries. The Fortinet breach underscores that no organisation, not even cyber security firms, is immune.
RipperSec Alliance with global hacking Groups
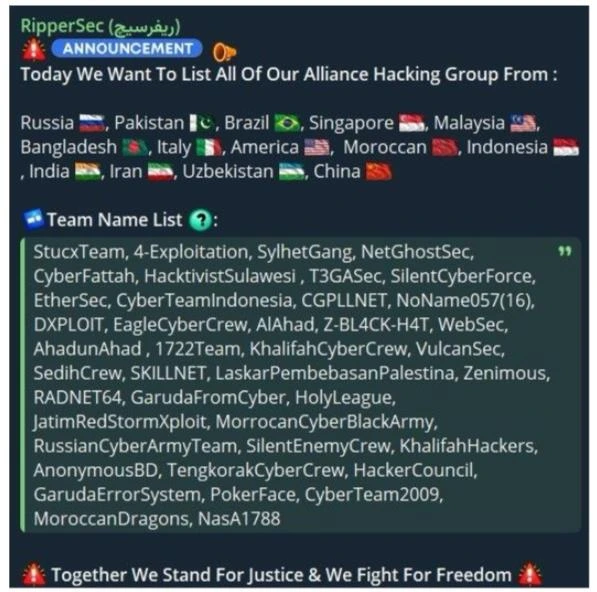
RipperSec has announced an alliance with global hacking groups spanning 14 countries, including Russia, Pakistan, Brazil, Singapore, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Italy, the United States, Morocco, Indonesia, India, Iran, Uzbekistan, and China.
This extensive network includes notable cyber collectives such as:
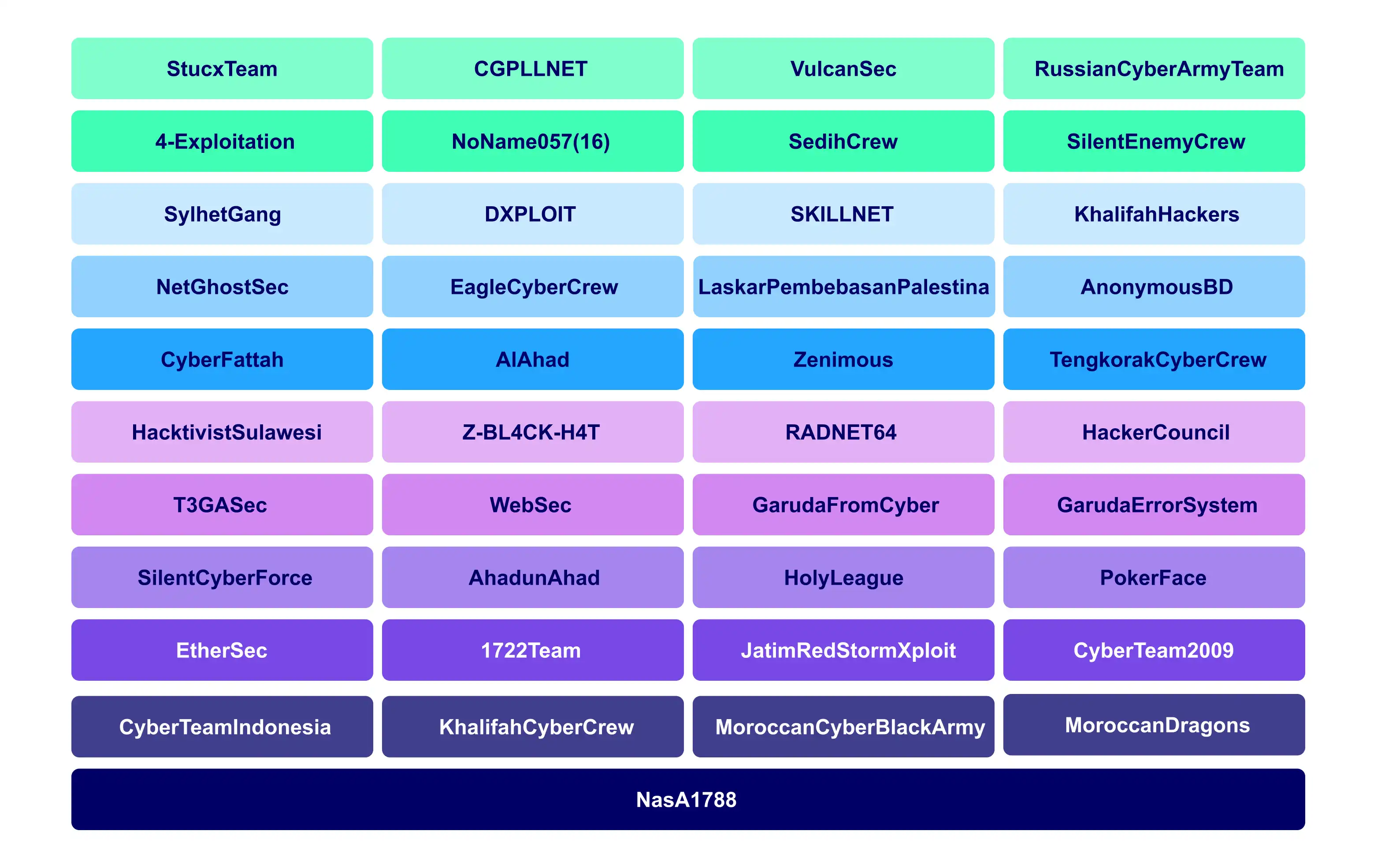
RipperSec is a prominent hacktivist group known for its extensive and growing influence within the global cybercrime ecosystem. The group operates under a decentralised structure, allowing it to collaborate with hacktivists and cyber criminals worldwide. This highlights a growing trend of collaboration between hacktivist groups that will amplify their attacks, particularly in terms of distributed denial of service (DDoS) which is RipperSec’s main type of attack. Many of these groups have been conducting attacks under #OpIsrael and #OpUkraine which both see attacks against European and NATO aligned countries. Collaboration between these groups is becoming more common as they have the same perceived aim of attacking “the west”.
AT&T Agrees to Pay $13 Million FCC Fine for Cloud Data Leak
Following the news in our July monthly summary revealing a major data breach that affected around 110 million customers. Now, AT&T has once again come under scrutiny for its handling of customer data following multiple breaches involving third-party vendors and cloud platforms. In the latest incident, AT&T agreed to pay $13 million in regulatory costs to settle an investigation by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). This investigation was launched after a data breach in early 2023, where a cloud vendor was hacked, exposing the information of 8.9 million AT&T Mobility customers. The exposed data included subscriber details from 2015 to 2017, such as the number of phone lines on an account, though sensitive information like Social Security numbers or credit card details was not compromised.
The FCC found that AT&T failed to enforce sufficient security measures for its vendors and did not ensure that the vendor deleted or returned customer data as contractually required. As part of the settlement, AT&T agreed to improve its internal data handling practices and enhance oversight of third-party vendors to prevent future breaches.
In July 2023, AT&T faced another significant breach related to its use of the Snowflake Inc. cloud platform, which exposed call and text metadata for nearly all of its mobile customers over several months in 2022. This breach affected about 109 million accounts. Additionally, a dark web leak in March 2023 compromised the personal details of 73 million AT&T customers, including sensitive data like Social Security numbers and account credentials.
These incidents underscore the growing threats posed by third-party vendors and cloud platforms in the telecommunications industry. The regulatory costs are mounting, with AT&T now required to pay millions in fines and invest in stronger compliance measures. FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel emphasised that telecommunications carriers have a responsibility to protect consumer data, which has become even more challenging in a digital age where data is often stored on third-party platforms.
In response to the increasing risks and regulatory costs, AT&T has committed to enhancing its data governance practices and tightening its oversight of third-party vendors. This case highlights how third-party threats can drive up regulatory penalties, as companies are held accountable not just for their own data handling, but also for the security practices of their supply chain. Failing to manage these risks can lead to severe financial repercussions, damage to a company’s reputation, and ongoing regulatory scrutiny.
These breaches also illustrate the growing importance of stronger supply chain oversight and better data governance. Companies are now being held accountable for third-party vulnerabilities, making it crucial for them to invest in compliance and security measures. The FCC has also emphasised the need for regular audits and stricter data management protocols to prevent such incidents in the future.
A Threat Actor Allegedly Has Leaked Over 10,800 Employees Data Belonging to Dell and Its Partners
.webp)
Dell Technologies has reportedly suffered two separate data breaches within a week, exposing sensitive data from over 10,000 employees. The hacker, using the alias "grep," first claimed responsibility for the breach on September 19, posting a sample of the stolen data on BreachForums and offering a full release for a nominal fee. According to grep, the exposed data includes employee names, IDs, and internal identifiers from Dell and its partners. This initial breach was described as “minor,” impacting approximately 10,800 employees.
Days later, on September 22, "grep" announced a second, more "significant" breach in collaboration with another hacker named “Chucky.” This time, 3.5 GB of internal files were stolen, allegedly including sensitive information from Dell’s Jira, Jenkins, and Confluence systems—tools often used in project management and development. The hacker also hinted that Dell's Atlassian tools were compromised to gain access to the data.
If this breach is legitimate, it could lead to further phishing or social engineering attacks, especially given recent trends in cybercriminal activities. While Dell has acknowledged the first breach to the media, it has not issued a public statement about either incident. Grep further teased Dell by referencing GDPR regulations, implying potential compliance risks for the company.
The hacker "grep" is believed to be aligned with hacktivist efforts and has been involved in numerous cyber attacks over the last two years, including a recent breach of CapGemini on September 9. Dell, already grappling with a large-scale breach in May that exposed the data of 49 million customers, has faced increasing scrutiny over its security protocols. The company’s response to these ongoing incidents remains under investigation.
Hackers inject malicious JS in Cisco store to steal credit cards, credentials
Cisco's company-themed merchandise site was offline after being compromised by a malicious JavaScript injection that steals sensitive customer information during checkout. Hackers inserted the code to capture details like credit card numbers, postal addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, and login credentials.
The breach appears to be linked to a CosmicSting attack (CVE-2024-34102), a vulnerability affecting the Adobe Commerce (Magento) shopping platform. This flaw allows attackers to read confidential data by injecting HTML or JavaScript into content management system (CMS) blocks in the checkout process.
The domain from which the malicious script is served, rextension[.]net, was registered on August 30. At the time of writing, Cisco’s stores in the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions remain unavailable, since it was the weekend. Though Cisco claims that no employee credentials were compromised, the risk remains as the attackers could potentially harvest employee login information.
In response, Cisco temporarily took the website offline and is working with the third-party supplier managing the site to resolve the issue. Cisco has notified affected users and continues to investigate.
A Cisco spokesperson confirmed, "The site has been taken offline as a precaution, and we are addressing the issue while notifying impacted users."
This breach underscores the vulnerabilities introduced by third-party platforms and highlights the need for stronger regulatory oversight and cyber security measures to mitigate third-party risks.
London Transport Cyber Attack
Transport for London (TfL) has been dealing with the aftermath of a significant cyber attack that occurred earlier this month, impacting its staff's access to key systems and email. The attack, which TfL reported to government agencies such as the National Cyber Security Centre and the National Crime Agency (NCA), has not yet shown evidence of customer data compromise. However, internal systems remain disrupted, affecting services like refunds for contactless card journeys and the ability to view journey histories for Oyster card users. Some live travel data, including train arrival information and TfL JamCams, is also temporarily unavailable on the website and app.
In response to the cyber attack, TfL has taken several internal measures, including suspending Oyster photocard applications and encouraging customers to self-serve online. TfL's Chief Technology Officer, Shashi Verma, apologised for the inconvenience and assured the public that efforts are underway to restore services as quickly as possible.
The attack has forced TfL to suspend its Dial-a-Ride booking system briefly, although existing bookings were honored, and essential bookings are being processed by phone. While public transport services continue to operate normally, TfL is taking extra precautions to secure its systems. Verma emphasised that TfL is closely monitoring system access to ensure only authorised personnel are permitted.
In a further development, the NCA arrested a 17-year-old male in Walsall in connection with the cyber attack. TfL is in the process of notifying around 5,000 customers whose bank account details may have been accessed, along with other personal information like names and contact details.
TfL has also confirmed that all 30,000 of its employees will need to attend in-person appointments to reset their passwords and verify their identities to regain access to TfL systems. The large-scale password reset is reminiscent of measures taken by other companies, such as DICK'S Sporting Goods, following a similar cyber security breach.
The attack comes after an earlier data breach in May 2023, when the Cl0p ransomware gang stole data belonging to approximately 13,000 TfL customers through a third-party supplier’s MOVEit file transfer service. While TfL initially reassured customers that no data was compromised in this recent incident, it later revealed that some personal data, including names, contact information, and addresses, was accessed. However, no sensitive information such as bank details or home addresses appears to have been compromised.
On 26th September, it was reported that 20 rail stations within the UK suffered cyber attacks against their public Wi-Fi captive portals. Initial reports suggest that the portals were defaced by a likely anti-immigration hacktivist group.
Rasomware groups targeting financial entities in September
_0.webp)
Ransomware vs Finance (last three monthes)

Cyber Risk
We bring the best of our collective experience, energy and creative power to fiercely safeguard our clients and fortify their communities.

Thomas Murray cyber alerts
Subscribe to stay up to date with developing threats in the cyber landscape
Insights

Ransomware at Europe’s Airports: Case for Community-Driven Third Party Risk Management
The recent ransomware attack on Collins Aerospace’s Muse software, which brought chaos to airports across Europe, serves as a stark reminder of a critical gap in how organisations approach Third Party Risk Management (TPRM).

JLR Cyber Attack: What it Means for Private Equity, Credit, and Equity Investments
From the iconic E-Type Jaguar to images of the late Queen driving modern Range Rovers on her estate, JLR has long held a uniquely British place in the national consciousness, even under Tata ownership. The incident has affected the owners of the business, the supply chain, and customers, and offers learnings for the Private Equity (PE) industry.

Impact of Cyber and Operational Resilience on Private Equity and Their Portfolio Companies
Implementing cyber and operational resilience measures is a strategic imperative for PE firms and their PortCos, enabling them to reduce the impact of cyber risks on asset valuations.

How Private Equity Leaders Turn Cyber Security Investment into Competitive Advantage
Leading firms are discovering something counterintuitive: investing in cyber security creates advantages worth far more than just protection.


