Thousands of Palo Alto Networks firewalls breached as attackers exploit critical vulnerabilities
Palo Alto Networks is a leading cyber security company that provides advanced security solutions to protect organisations against cyber threats. Its offerings include next-generation firewalls, cloud security tools, endpoint protection, and artificial intelligence-driven threat intelligence. The company's products and services are designed to secure networks, cloud environments, and endpoints, enabling organizations to prevent and respond to cyberattacks effectively.
Thousands of Palo Alto Networks firewalls were recently exploited due to two critical vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474, which allow attackers to bypass authentication and escalate privileges. The flaws were initially used to compromise about 2,000 devices, though this number has since decreased to 800. Attackers deployed web shells, cryptominers, and other malware to gain remote control of the devices. Exploitation surged after a proof-of-concept exploit became publicly available.


The vulnerabilities enable attackers to chain authentication bypass with privilege escalation, facilitating remote code execution on the PAN-OS management interface. Exploitation requires network access to the interface, and the attackers have leveraged tools like Sliver implants for control. Some of these implants have been reused across multiple compromised devices, indicating prolonged and opportunistic activity. Investigators suspect several threat actors, given the widespread availability of exploit code.
Palo Alto Networks urges customers to secure their devices by restricting management interface access, enforcing strong authentication practices, and monitoring logs for suspicious activity. The company is actively investigating the scope of the attack, which, while affecting a small percentage of devices globally, represents a significant security risk.
Thomas Murray's cyber threat intelligence team has found another common vulnerability exploited CVE-2024-3400, a critical vulnerability in Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS, specifically affecting the GlobalProtect feature. This vulnerability is a command injection flaw that allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on affected firewalls. It has been assigned a CVSSv4.0 score of 10, indicating its high severity.
The vulnerability primarily impacts specific versions of PAN-OS where both the GlobalProtect gateway and device telemetry are enabled. If these features are not activated, the vulnerability cannot be exploited.
https://www.theregister.com/2024/11/22/palo_alto_firewalls_under_exploit/
Chinese Cyber-Attack Targets T-Mobile in Major Telecom Breach
T-Mobile's network was compromised in a significant cyber-espionage attack linked to Salt Typhoon, a Chinese state-sponsored hacking group. This breach was part of a broader campaign targeting several major U.S. telecommunications companies, including AT&T, Verizon, and Lumen Technologies, as well as international telecom firms. The attack was reportedly focused on infiltrating critical systems used for law enforcement surveillance, potentially exposing sensitive communications, such as unencrypted messages and audio. While T-Mobile claims no major impact on its systems or customer data, does not have a good track record when it comes to cyber security. Just last month, it paid a $31.5 million settlement to resolve multiple data breaches that took place over three years, the breach raises concerns about the theft of sensitive metadata and personal communications, particularly regarding high-ranking officials involved in national security into the breach suggest that Salt Typhoon exploited vulnerabilities in telecom infrastructure, notably through Cisco Systems routers, to gain access to call records, surveillance data, and other sensitive information. The group's advanced use of artificial intelligence further enabled their intelligence-gathering efforts, with some targets including U.S. government officials. This breach is especially troubling given the national security implications, as hackers may have gained insight into critical government communications.
The attack hi weaknesses in the telecommunications sector, which is considered critical infrastructure under U.S. law. Federal agencies, including the FBI and CISA, are continuing to investigate, while the Biden administration has issued warnings about the breach's potential impact. In response, T-Mobile is reportedly strengthening its defenses, including adopting zero-trust architecture and enhancing authentication measures. Despite these efforts, experts warn that the full extent of the damage may not be known for some time.
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/tmobile-breached-chinese/
New SteelFox Malware Impersonates Popular Software to Harvest Browser Data
Cyber security researchers at Securelist have uncovered a new malware campaign dubbed "SteelFox," which has been actively spreading through online forums, torrent trackers, and blogs. This malware, masquerading as popular legitimate software such as Foxit PDF Editor, AutoCAD, and JetBrains, primarily targets Microsoft Windows users who are engaged in downloading pirated software or fake activation tools, commonly known as cracks. The campaign began in February 2023 and has infected over 11,000 users worldwide. SteelFox combines cryptocurrency mining and data-stealing functionalities, with a focus on extracting sensitive personal information, including credit card details, browsing history, login credentials, and system information such as installed software and network configurations.
SteelFox operates through a multi-stage attack process. It starts with a malicious "dropper" disguised as a software activator, which requires administrator privileges to execute. Once installed, the malware sets itself up as a Windows service, ensuring it persists even after system reboots. To escalate its privileges, SteelFox exploits vulnerable drivers and hides its malicious components using AES-128 encryption. It communicates securely with command servers using TLS 1.3 and SSL pinning to avoid detection and protect its data exfiltration. The malware's use of modern C++ programming and external libraries adds to its sophistication, making it a powerful tool in the hands of cybercriminals.
The malware has affected users across over 10 countries, including the UAE, India, Brazil, China, and Russia, among others. The impact of SteelFox highlights the risks associated with downloading software from unofficial sources, particularly for organisations. Experts, including James McQuiggan from KnowBe4, stress the importance of verifying software origins and maintaining strong cyber security practices, such as using endpoint protection, applying security patches, and educating users about the dangers of unverified software. To protect against SteelFox, users should avoid downloading software from untrusted sites and ensure they have a robust security solution in place to detect and prevent the installation of malicious software.
https://hackread.com/steelfox-malware-software-to-steal-browser-data/
Finastra, the financial software company, is currently investigating a data breach that has raised concerns about the security of its systems.
Finastra, a major UK-based fintech firm, is currently investigating a data breach after a hacker, known by the moniker 'abyss0', claimed to have stolen data from the company and offered it for sale on a dark web forum. The breach was first identified when suspicious activity was detected on Finastra's internal file-transfer application used for exchanging data with customers. The company promptly isolated the affected platform and enlisted a third-party cyber security firm to investigate. Initial findings suggest the breach was caused by compromised credentials, although the specific source of the compromise remains under investigation.
Finastra confirmed that no ransomware or malware was involved in the attack, and there has been no direct impact on customer operations or systems. The company reassured customers that the affected platform was not the default application for file exchanges, and not all customers were using it. While Finastra works to verify the affected clients, it has emphasized transparency and accuracy in its communications with them. The hacker claimed to have stolen 400 GB of data from the company's systems, which may include sensitive customer information. However, the hacker's attempts to sell the stolen data have since been removed from the forum, suggesting either a successful sale or a retreat.
Finastra provides software to approximately 8,000 financial institutions worldwide, including major banks and credit unions. The company’s technology is integral to many financial operations, making the breach a significant concern for the financial sector. As of now, Finastra continues to investigate the incident and coordinate with affected parties. The investigation is ongoing, and the company has stated that it will continue to update customers as more information becomes available.
https://www.securityweek.com/financial-software-firm-finastra-investigating-data-breach/
Schneider Electric Hacked and Blackmailed Following Lumma Infostealer Infection
On November 4th, Schneider Electric confirmed a data breach in which hackers stole 40GB of data from the company’s Jira server. The attack, attributed to a new ransomware group called “HellCat,” targeted the company’s project execution tracking platform. HellCat, a group comprising several well-known hackers, including "grep," demanded $125,000 to delete the stolen data and prevent it from being publicly released.
The breach was traced back to an employee who had been infected by the Lumma Infostealer malware on October 13, 2024. The infection likely occurred when the employee downloaded a cracked version of Adobe Premiere from a YouTube video. Hudson Rock researchers traced the compromised credentials, which were used to access the Jira server. Once inside, the hackers scraped 400,000 rows of sensitive user data, including email addresses and names of Schneider Electric employees and customers.
The breach exposed weaknesses in Schneider Electric’s cyber security practices, including a lack of anti-virus protection and poor password hygiene among its employees. The breach highlights the growing risk of infostealers and the importance of organisations strengthening their security measures, such as implementing multi-factor authentication and better employee training. Collaborative tools like Jira and Confluence remain prime targets for cybercriminals due to the wealth of sensitive information they contain.
Australian Cyber Security Act passed into law
Australia has passed its first standalone Cyber Security Act as part of its 2023–2030 Cyber Security Strategy, aimed at improving the nation’s cyber resilience and positioning Australia as the most cyber-secure country globally. The new legislation includes a “limited use” obligation, which restricts how the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) and the National Cyber Security Coordinator can use information shared by organisations after cyber incidents, encouraging businesses to report attacks without fear of penalties.
Key initiatives in the act include mandatory reporting of ransom payments by organisations, which will help cyber security professionals understand cybercriminal behavior. The legislation also mandates the creation of a Cyber Incident Review Board (CIRB) to conduct post-incident reviews and recommend improvements. Additionally, the act will set standards for the cybersecurity of smart devices and reform the Security of Critical Infrastructure Act 2018 (SOCI) to simplify government-industry information sharing and enhance government powers in the event of a major cyber attack on critical infrastructure. These efforts aim to strengthen Australia’s defenses against cyber threats and foster collaboration between government and industry.
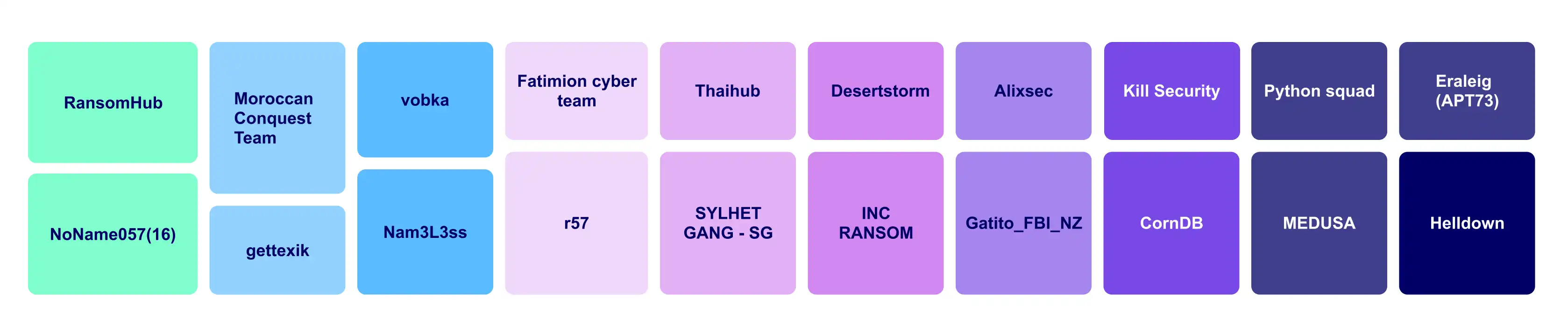
Threat actors targeting financial entities in October 2024
%2009.12.webp)
Ransomware vs Finance (last three months)

Cyber Risk
We bring the best of our collective experience, energy and creative power to fiercely safeguard our clients and fortify their communities.

Thomas Murray cyber alerts
Subscribe to stay up to date with developing threats in the cyber landscape
Insights

Ransomware at Europe’s Airports: Case for Community-Driven Third Party Risk Management
The recent ransomware attack on Collins Aerospace’s Muse software, which brought chaos to airports across Europe, serves as a stark reminder of a critical gap in how organisations approach Third Party Risk Management (TPRM).

JLR Cyber Attack: What it Means for Private Equity, Credit, and Equity Investments
From the iconic E-Type Jaguar to images of the late Queen driving modern Range Rovers on her estate, JLR has long held a uniquely British place in the national consciousness, even under Tata ownership. The incident has affected the owners of the business, the supply chain, and customers, and offers learnings for the Private Equity (PE) industry.

Impact of Cyber and Operational Resilience on Private Equity and Their Portfolio Companies
Implementing cyber and operational resilience measures is a strategic imperative for PE firms and their PortCos, enabling them to reduce the impact of cyber risks on asset valuations.

How Private Equity Leaders Turn Cyber Security Investment into Competitive Advantage
Leading firms are discovering something counterintuitive: investing in cyber security creates advantages worth far more than just protection.


