Advanced Fined £3 Million for 2022 Ransomware Attack
In August 2022, UK-based IT provider Advanced suffered a ransomware attack that severely impacted healthcare services, particularly the NHS 111 helpline. The breach affected critical systems, forcing healthcare providers to rely on manual processes and prompting a government-level emergency response. Attackers gained access through an exposed remote access tool, exploiting security gaps, including the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
The Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) conducted an investigation and found that Advanced had failed to implement adequate cybersecurity protections, leaving sensitive patient and operational data vulnerable. The attack exposed personal data of 79,404 individuals, raising concerns about the security of outsourced healthcare IT services.


As a result, the ICO initially proposed a £6 million fine, but Advanced reached a settlement to pay £3.1 million. The case highlights the risks of inadequate security in critical infrastructure and reinforces the need for robust MFA, network segmentation, and proactive threat monitoring to protect against ransomware attacks.
https://therecord.media/advanced-fined-3-million-ransomware-attack-ico
Blind Eagle APT Intensifies Cyberattacks on Colombian Government
A sophisticated cyber espionage and financial crime group known as Blind Eagle (APT-C-36) has ramped up attacks against Colombian government agencies and private sector organisations in a campaign that began in November 2024. The threat actor, believed to operate primarily in Latin America, is known for its aggressive and persistent targeting of institutions within Colombia, often focusing on government, finance, and law enforcement sectors.
Blind Eagle’s latest campaign leverages a vulnerability identified as CVE-2024-43451, which allows attackers to capture Windows NTLMv2 hashes, enabling credential theft and unauthorised access. Check Point researchers uncovered evidence that this exploit was actively used to infiltrate systems and establish persistent access to sensitive Colombian networks.
The group's attack chain includes:
- Spear-phishing emails masquerading as official government communications.
- Malicious attachments that execute scripts to exploit the NTLMv2 vulnerability.
- Credential harvesting from compromised networks to escalate privileges.
- Deployment of remote access trojans (RATs) for continued access and data exfiltration.
Blind Eagle is known for its rapid infection rates. In just one campaign around December 19, 2024, over 1,600 victims were affected, a significant number for a group that usually relies on highly targeted attacks.
While Blind Eagle has long been associated with cyber espionage, researchers note that the group also engages in financially motivated attacks, blurring the line between nation-state operations and cybercriminal activities. There is speculation that the group may have connections to criminal organisations in Latin America, though concrete ties have not been confirmed.
The attacks have disrupted government services, raised concerns about data breaches, and forced agencies to increase cyber security measures. The Colombian government has urged rapid patching and security enhancements, but Blind Eagle continues to evolve its tactics, using new exploits and sophisticated techniques.
This campaign highlights the increasing cyber threats facing Latin American institutions, particularly from groups that combine espionage and financial motives. With Blind Eagle demonstrating an ability to rapidly compromise large numbers of victims, the need for proactive security measures has never been greater.
https://www.darkreading.com/cyberattacks-data-breaches/apt-blind-eagle-targets-colombian-government
North Korean Hacker Group 'TraderTraitor' Implicated in $1.5 Billion Bybit Cryptocurrency Heist
In March 2025, Safe{Wallet}, a multi-signature (multisig) cryptocurrency platform, disclosed that the $1.5 billion theft from the Bybit exchange was orchestrated by the North Korean-affiliated hacker group known as TraderTraitor (also referred to as Jade Sleet, PUKCHONG, and UNC4899). This sophisticated, state-sponsored attack involved the compromise of a Safe{Wallet} developer's macOS laptop, identified as 'Developer1'.
The breach began on February 4, 2025, when Developer1 downloaded a Docker project named "MC-Based-Stock-Invest-Simulator-main," likely obtained through a social engineering scheme. This project communicated with the domain "getstockprice[.]com," registered two days prior via Namecheap. Historically, TraderTraitor has employed similar tactics, deceiving cryptocurrency exchange developers into downloading malicious Docker projects under the guise of troubleshooting assistance via platforms like Telegram.
Once the malware was executed on Developer1's machine, it facilitated reconnaissance of Safe{Wallet}'s Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment. The attackers hijacked active AWS session tokens, effectively bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA) controls. They operated using Developer1's AWS credentials, originating from ExpressVPN IP addresses with User-Agent strings indicative of Kali Linux usage—a distribution tailored for offensive security operations.
To maintain access and obfuscate their presence, the attackers employed several advanced techniques:
- Malware Deployment: Utilised the open-source Mythic framework for command and control operations.
- Website Compromise: Injected malicious JavaScript into the Safe{Wallet} website between February 19 and 21, 2025, potentially targeting users or further internal systems.
- Anti-Forensic Measures: Deleted malware artifacts and cleared Bash history on the compromised developer's machine to hinder investigative efforts.
Bybit's CEO, Ben Zhou, reported that of the stolen $1.5 billion:
- Approximately 77% of the funds remain traceable.
- 20% have become untraceable, likely laundered or mixed to obscure their origin.
- 3% have been successfully frozen, thanks to collaborative efforts with entities such as Mantle, Paraswap, and blockchain investigator ZachXBT.
Notably, about 83% of the stolen assets (equivalent to 417,348 ETH) were converted into Bitcoin and distributed across nearly 7,000 wallets, complicating tracking and recovery operations.
The Bybit heist contributes significantly to a troubling trend in 2025, with Web3 projects experiencing losses totaling $1.6 billion in just the first two months—an eightfold increase compared to the same period in the previous year, as reported by blockchain security platform Immunefi. This surge underscores the escalating sophistication of cyber threats targeting the cryptocurrency sector.
https://thehackernews.com/2025/03/safewallet-confirms-north-korean.html
Certificate Expiry Causes Chromecast 2nd Gen and Audio Devices to Malfunction
In March 2025, users of Google's second-generation Chromecast and Chromecast Audio devices began encountering "Untrusted device" errors, rendering their devices inoperable. The issue was traced to an expired intermediate Certificate Authority (CA) that had reached its ten-year validity on March 9, 2025. This expiration prevented Google's servers from authenticating the affected devices, leading to the observed errors.
Google acknowledged the problem and advised users against performing factory resets, as this could exacerbate the issue by making devices unable to re-establish connections. The company committed to developing a fix and provided updates through its Nest Community page.
By mid-March, Google began rolling out an update via the Google Home app (version 3.30.1.6 for Android and 3.30.106 for iOS) to address the malfunction. Users were instructed to keep their devices connected to receive the update, which aimed to restore full functionality to the impacted Chromecasts.
This incident underscores the importance of timely certificate management in maintaining device operability and highlights the potential challenges users face with expired security credentials in connected devices.
Microsoft Warns of Malvertising Campaign Infecting Over 1 Million Devices Worldwide
In early December 2024, Microsoft identified a large-scale malvertising campaign, tracked as Storm-0408, which compromised over one million devices globally. This campaign utilised malicious advertisements on illegal streaming websites to deliver malware aimed at stealing sensitive information.
The attack began with users visiting illegal streaming sites embedded with malvertising redirectors. These redirectors led users through a multi-layered redirection chain, eventually directing them to intermediary websites that hosted malicious payloads on platforms like GitHub, Discord, and Dropbox. Notably, GitHub was used to host dropper malware responsible for deploying additional malicious programs, including Lumma Stealer and Doenerium, which are designed to collect system information.
The infection process involved multiple stages:
- First Stage: Establishing a foothold on target devices.
- Second Stage: Conducting system reconnaissance, collecting data, and delivering additional payloads.
- Third Stage: Executing commands, deploying further payloads, evading defenses, maintaining persistence, communicating with command-and-control servers, and exfiltrating data.
- Fourth Stage: Utilising PowerShell scripts to configure Microsoft Defender exclusions and executing commands to download data from remote servers.
The attackers employed various scripts and leveraged legitimate system tools (Living-off-the-Land Binaries and Scripts - LOLBAS) such as PowerShell.exe, MSBuild.exe, and RegAsm.exe for command-and-control communications and data exfiltration.
This campaign underscores the risks associated with visiting illegal streaming websites, which are often laden with malicious advertisements. Users are advised to exercise caution and avoid such sites to mitigate the risk of malware infections. Organisations should implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular system updates, employee training on phishing and malvertising tactics, and the use of reputable security software to detect and prevent such threats.
Microsoft's disclosure highlights the evolving tactics of cybercriminals and the importance of vigilance in the face of sophisticated malvertising campaigns.
https://thehackernews.com/2025/03/microsoft-warns-of-malvertising.html
Exploitation of PHP-CGI RCE Vulnerability CVE-2024-4577 in Targeted Attacks on Japanese Sectors
In early 2025, cybersecurity researchers identified a series of targeted cyberattacks against Japanese organisations in the technology, telecommunications, entertainment, education, and e-commerce sectors. These attacks exploited a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2024-4577, in the PHP-CGI implementation on Windows systems.
CVE-2024-4577 is an argument injection flaw in PHP's CGI implementation on Windows platforms. This vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to bypass previous security measures, notably those addressing CVE-2012-1823, by leveraging specific character sequences. Successful exploitation enables remote execution of arbitrary code on affected servers.
The attackers initiated their campaign by exploiting CVE-2024-4577 to gain initial access to target systems. Upon successful infiltration, they executed PowerShell scripts to deploy Cobalt Strike's reverse HTTP shellcode, establishing persistent remote access. Subsequent stages involved:
- Reconnaissance and Privilege Escalation: Utilising tools such as JuicyPotato, RottenPotato, and SweetPotato to elevate privileges within the compromised environment.
- Lateral Movement: Employing utilities like Fscan and Seatbelt to navigate through the network and identify additional targets.
- Persistence Mechanisms: Modifying Windows Registry entries, creating scheduled tasks, and deploying custom services using Cobalt Strike plugins, notably 'TaoWu', to maintain long-term access.
- Log Erasure: Executing wevtutil commands to delete event logs, effectively removing traces of their activities from Windows security, system, and application logs.
- Credential Theft: Running Mimikatz to extract and exfiltrate passwords and NTLM hashes from the system memory of compromised machines.
While the primary focus of these attacks was on Japanese organisations, similar exploitation attempts were observed globally. Notably, Taiwan experienced a significant concentration of attacks, accounting for approximately 54.65% of detected incidents. Other affected regions included Hong Kong (27.06%), Brazil (16.39%), Japan (1.57%), and India (0.33%).
This campaign underscores the critical importance of timely vulnerability management and proactive security measures to defend against sophisticated cyber threats.
https://thehackernews.com/2025/03/php-cgi-rce-flaw-exploited-in-attacks.html
Silk Typhoon's Shift to IT Supply Chain Attacks
In March 2025, Microsoft Threat Intelligence reported a strategic shift in the tactics of Silk Typhoon (also known as HAFNIUM), a Chinese state-sponsored espionage group. The group has expanded its focus to include the exploitation of IT supply chains, targeting sectors such as information technology services, remote monitoring and management companies, managed service providers, healthcare, legal services, higher education, defense, government, non-governmental organisations, and energy.
Silk Typhoon has demonstrated advanced capabilities in understanding and manipulating cloud environments. Their tactics include:
- Exploitation of Edge Devices: Rapid exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities in public-facing devices to gain initial access.
- Credential and API Key Theft: Utilising stolen API keys and credentials from privilege access management, cloud app providers, and cloud data management companies to infiltrate downstream customer environments.
- Reconnaissance and Data Collection: Conducting thorough reconnaissance and data collection on targeted devices via administrative accounts, focusing on data related to U.S. government policy, legal processes, and law enforcement investigations.
The shift towards IT supply chain attacks underscores the necessity for organisations to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Recommendations include:
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly update and patch systems to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls and monitor the use of privileged accounts.
- Supply Chain Security: Assess and ensure the security practices of third-party vendors and partners.
This development highlights the evolving nature of cyber threats and the importance of proactive defense strategies to protect against sophisticated adversaries like Silk Typhoon.
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2025/03/05/silk-typhoon-targeting-it-supply-chain/
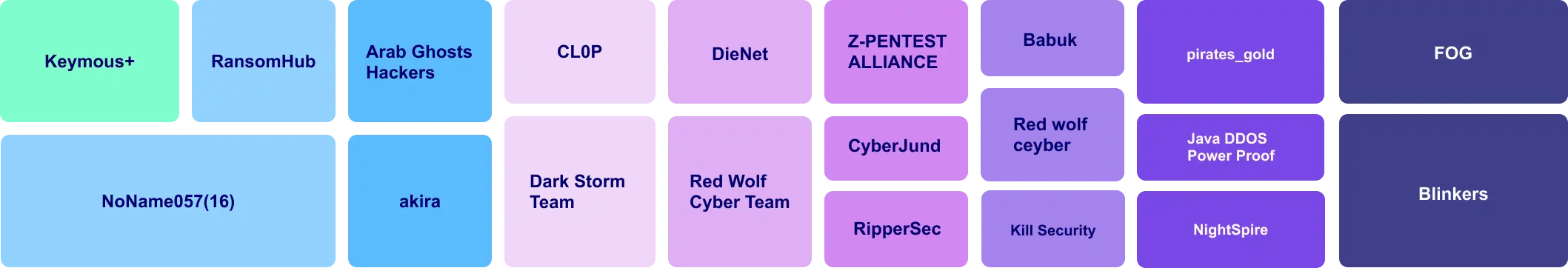
Threat actors targeting financial entities in March 2025
%2004.04.webp)
Ransomware vs Finance (last three months)

Cyber Risk
We bring the best of our collective experience, energy and creative power to fiercely safeguard our clients and fortify their communities.

Thomas Murray cyber alerts
Subscribe to stay up to date with developing threats in the cyber landscape
Insights
An EvilProxy deep dive: From Outlook to Teams, the £1m heist
A UK-based multinational professional services group narrowly avoided a £1M business email compromise after a patient adversary manipulated an existin


